How can you tell if a person is unresponsive and not breathing?
The person doesn't react to attempts of waking them up and doesn't breathe normally or at all.
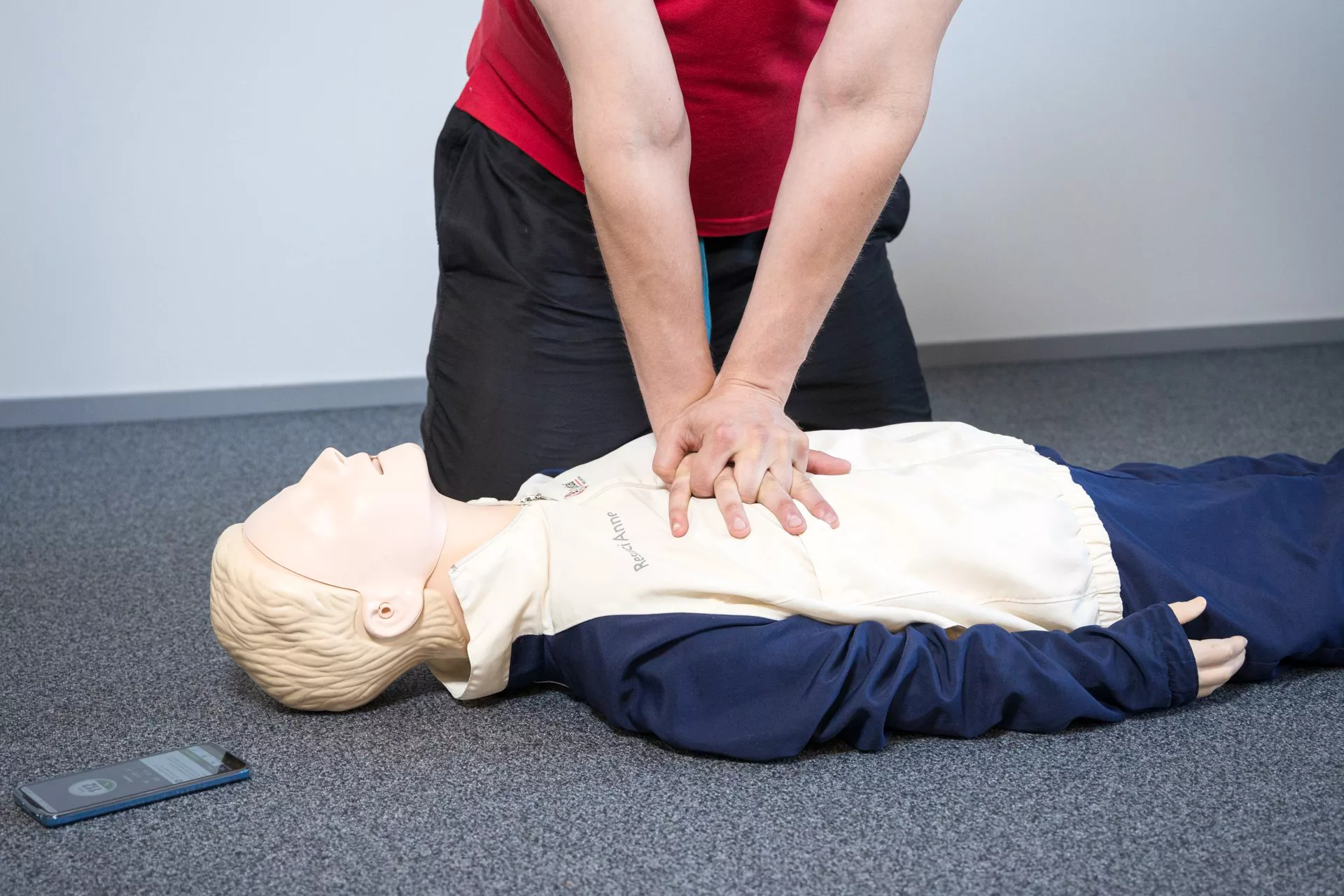
Resuscitation should be performed if the person’s heart has stopped. CPR can save a life.
How can you tell if a person is unresponsive and not breathing?
The person doesn't react to attempts of waking them up and doesn't breathe normally or at all.
When the heart stops, blood circulation in the brain ceases and every minute counts. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) aims to preserve blood circulation in the brain, thus preventing further damage and creating favourable conditions for the heart to resume beating. Timely CPR can triple a person’s chance of survival.
If there are multiple first-aiders present, take turns performing CPR and switch every couple of minutes.
If you have access to a defibrillator and there are multiple first-aiders on the scene, send one to get the defibrillator, switch it on and follow the instructions. The others should continue taking turns performing CPR.
If the unresponsive person was rescued from water, always start resuscitation with five rescue breaths. Then continue with cycles of 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths until paramedics arrive or the person recovers.